In recent years, technology has dramatically transformed the way we respond to and manage disasters. Tech-enabled disaster response leverages advanced tools and systems to improve preparedness, coordination, and recovery efforts during and after emergencies. This article explores the role of technology in disaster response, including its applications, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.

The Role of Technology in Disaster Response
- Early Warning Systems:
- Meteorological Forecasting: Advanced meteorological tools use satellite data, radar, and weather models to provide early warnings for natural disasters such as hurricanes, tornadoes, and floods. These systems help authorities issue timely alerts and evacuations.
- Seismic Monitoring: Earthquake early warning systems rely on seismic sensors to detect the initial, less-damaging seismic waves and provide warnings before the more destructive waves arrive. This technology can give people valuable seconds to minutes to take cover or shut down critical systems.
- Communication Tools:
- Emergency Alert Systems: Technologies like wireless emergency alerts (WEA) and mass notification systems allow authorities to send critical information to the public through text messages, emails, and phone calls. These systems ensure that people receive timely updates about disaster developments and safety instructions.
- Social Media: Social media platforms are increasingly used to disseminate information quickly and efficiently during disasters. They enable real-time communication between emergency responders, affected communities, and the general public, facilitating information sharing and coordination.
- Geospatial Technologies:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS technology helps map disaster-affected areas, analyze damage, and plan response strategies. By integrating spatial data with other information sources, GIS supports decision-making and resource allocation during emergencies.
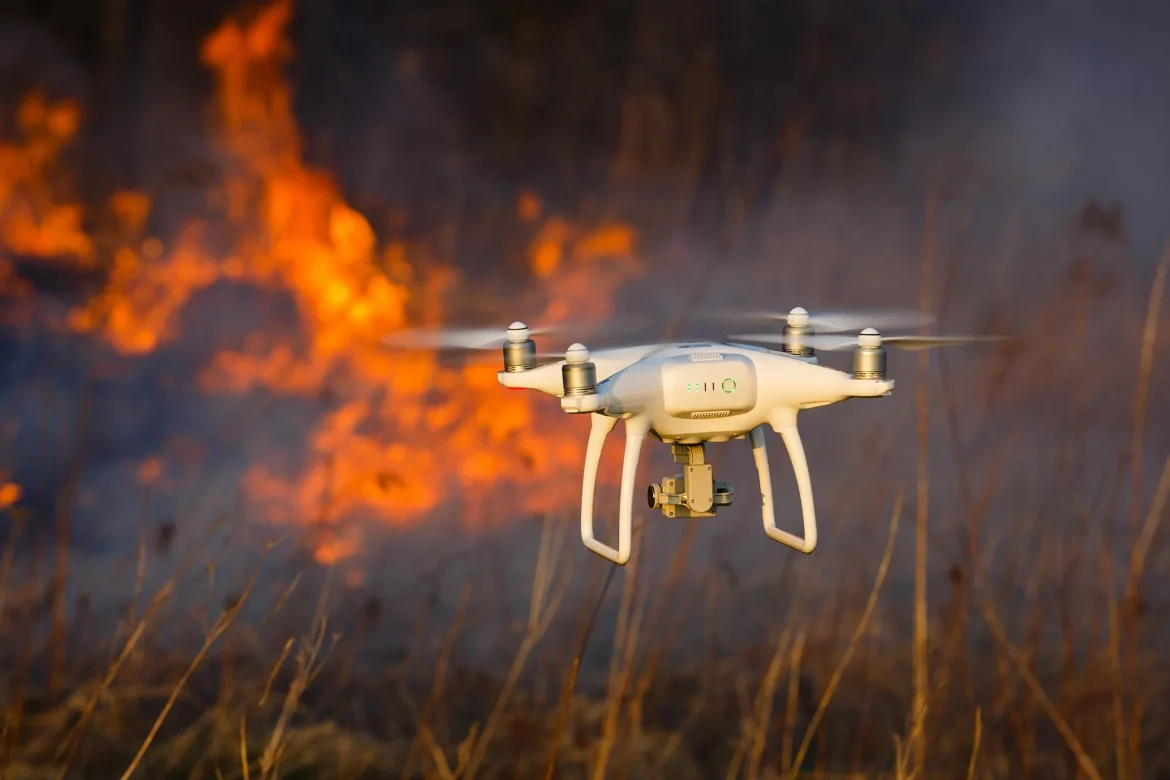
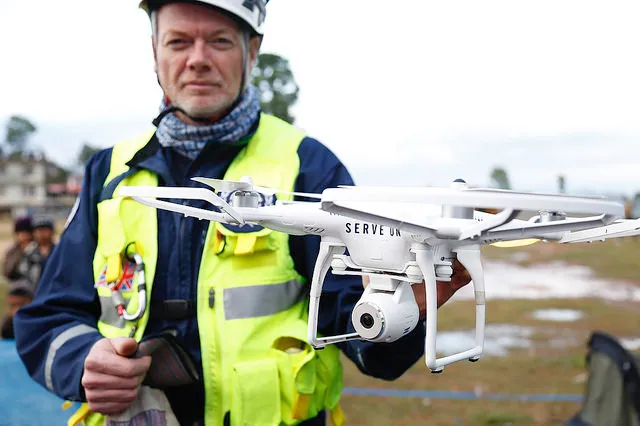
- Drones: Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) or drones are used for aerial surveys, damage assessment, and search and rescue operations. Drones provide real-time imagery and data, offering a bird’s-eye view of affected areas and identifying hotspots that may require immediate attention.
- Data Analytics:
- Predictive Modeling: Data analytics and machine learning models can predict disaster impacts, assess risks, and optimize response strategies. By analyzing historical data and current conditions, these models help forecast potential scenarios and guide decision-making.
- Situation Awareness: Real-time data from various sources, including sensors and satellite imagery, is analyzed to provide situational awareness. This information helps responders understand the scope of the disaster, track the movement of hazards, and identify areas in need of assistance.
- Resource Management:
- Logistics Software: Advanced logistics and supply chain management software help coordinate the distribution of resources, such as food, medical supplies, and personnel. These tools ensure that aid reaches the areas most in need and track the status of shipments and inventory.
- Crowdsourcing Platforms: Platforms that allow citizens to contribute information about disaster impacts, needs, and resources help supplement official data. Crowdsourcing provides valuable insights into affected areas and enhances the coordination of relief efforts.
Benefits of Tech-Enabled Disaster Response
- Improved Efficiency:
- Faster Response Times: Technology streamlines communication and coordination among responders, reducing delays and improving response times. Early warnings and real-time data enable quicker decision-making and more effective deployment of resources.
- Enhanced Coordination: Integrated systems and data sharing platforms improve coordination between various agencies, organizations, and volunteers. This reduces duplication of efforts and ensures a more organized response.
- Enhanced Safety:
- Risk Mitigation: Predictive modeling and early warning systems help mitigate risks by providing advance notice of potential disasters. This allows individuals and communities to take preventive measures and evacuate if necessary.
- Rescue Operations: Drones and other technologies improve search and rescue operations by providing detailed information about affected areas and locating survivors more efficiently.
- Better Resource Allocation:
- Targeted Assistance: Data-driven insights enable more precise allocation of resources, ensuring that aid reaches the areas and populations most in need. This minimizes waste and maximizes the impact of relief efforts.
- Optimized Logistics: Advanced logistics and supply chain management tools help streamline the distribution of resources, reducing bottlenecks and ensuring timely delivery of essential supplies.
- Informed Decision-Making:
- Data-Driven Insights: Real-time data and predictive models provide valuable information for decision-making, allowing responders to make informed choices about resource allocation, evacuation plans, and recovery strategies.
- Situational Awareness: Comprehensive situational awareness enhances understanding of the disaster’s scope and impact, supporting more effective response and recovery efforts.
Challenges and Considerations
- Data Privacy and Security:
- Protection of Sensitive Information: The collection and use of personal data during disasters raise concerns about privacy and security. Ensuring that data is protected and used responsibly is essential to maintain public trust.
- Cybersecurity Risks: The increased reliance on technology for disaster response also introduces cybersecurity risks. Protecting communication and data systems from cyberattacks is crucial for maintaining operational integrity.
- Technology Accessibility:
- Digital Divide: Not all communities have equal access to technology, which can create disparities in disaster response and recovery efforts. Addressing the digital divide and ensuring that technology benefits all populations is important for equitable disaster management.
- Infrastructure Limitations: In some regions, infrastructure limitations may affect the deployment and effectiveness of tech-enabled solutions. Ensuring that technology is adapted to local conditions and resources is essential.
- Integration and Interoperability:
- System Compatibility: Integrating various technologies and systems used by different agencies and organizations can be challenging. Ensuring interoperability and seamless data sharing is crucial for effective coordination and response.
- Training and Expertise: Effective use of tech-enabled solutions requires specialized training and expertise. Ensuring that responders are adequately trained to use new technologies is essential for maximizing their benefits.
Future Trends in Tech-Enabled Disaster Response
- Advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- Enhanced Predictive Models: AI and machine learning will continue to advance predictive modeling, improving the accuracy of forecasts and risk assessments. These technologies will enhance situational awareness and support more effective response strategies.
- Automated Systems: AI-driven automation will play a greater role in streamlining response operations, including resource allocation, damage assessment, and communication.
- Increased Use of IoT Devices:
- Smart Sensors: The Internet of Things (IoT) will expand the use of smart sensors for monitoring environmental conditions, infrastructure health, and resource usage. These devices will provide real-time data for more proactive and responsive disaster management.
- Connected Systems: IoT devices will enhance connectivity between various systems and platforms, improving data sharing and coordination among responders and agencies.
- Enhanced Public Engagement:
- Citizen Participation: Technology will increasingly involve citizens in disaster response efforts through crowdsourcing, mobile apps, and social media platforms. Engaging the public will enhance information sharing and support community-based responses.
- Education and Awareness: Technology will also be used to educate and raise awareness about disaster preparedness and response, empowering individuals and communities to take proactive measures.

Conclusion
Tech-enabled disaster response has transformed emergency management by providing advanced tools and systems for early warning, communication, data analysis, and resource management. The integration of technology enhances efficiency, safety, and coordination during disasters, leading to more effective responses and recovery efforts. While challenges related to data privacy, accessibility, and system integration persist, ongoing advancements and future trends promise to further enhance the capabilities of tech-enabled disaster response. As technology continues to evolve, it will play a pivotal role in improving disaster preparedness and resilience, ultimately saving lives and reducing the impact of emergencies.


