Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming various industries, and the realm of art and creativity is no exception. From generating stunning visual artworks to composing music and crafting written content, AI is redefining what is possible in the creative world. This article delves into how AI is influencing art and creativity, exploring its applications, benefits, challenges, and the implications for the future of artistic expression.
Understanding AI in Art and Creativity
- What is AI in Art?
- Definition: AI in art involves the use of artificial intelligence technologies to create, enhance, or interpret artworks. This can include generating visual art, composing music, writing poetry, and even creating interactive installations. AI systems utilize algorithms and machine learning to process and produce creative outputs that mimic or innovate upon human artistic practices.
- Core Technologies: Key technologies driving AI in art include Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), neural networks, and natural language processing. GANs, for instance, can create new images by learning from existing ones, while neural networks can compose music and write text based on patterns and styles.
- How AI Enhances Artistic Creation:
- Data Analysis and Pattern Recognition: AI systems analyze vast amounts of data to recognize patterns and generate new content. For instance, AI can study the styles of famous artists and produce new works that reflect those styles or blend multiple styles.
- Algorithmic Creativity: AI can employ algorithms to generate unique artistic outputs. By adjusting parameters and inputs, AI can create an endless variety of artistic forms, from abstract paintings to realistic portraits.
Applications of AI in Art and Creativity
- Visual Art:
- AI-Generated Artworks: AI algorithms can generate original visual art by processing and combining elements from existing artworks. This includes creating new paintings, digital art, and illustrations. Notable examples include works created by AI systems like DeepArt and DALL-E, which produce art based on user inputs or predefined styles.
- Style Transfer: AI can apply the style of one artwork to another image through a process known as style transfer. This technique enables artists to merge their creations with the aesthetics of famous artworks, producing novel visual experiences.
- Music Composition:
- AI-Generated Music: AI systems can compose music by analyzing patterns in existing compositions and generating new melodies, harmonies, and rhythms. Tools like OpenAI’s MuseNet and AIVA (Artificial Intelligence Virtual Artist) create original music across various genres and styles.
- Interactive Music Systems: AI-driven interactive systems can respond to live input, creating dynamic and adaptive musical experiences. These systems can be used in live performances, video games, and immersive installations, enhancing audience engagement.
- Writing and Literature:
- AI-Generated Text: AI can generate written content, including poetry, prose, and articles, by learning from large datasets of text. Examples include GPT-3 and similar language models, which can produce coherent and contextually relevant text based on prompts provided by users.
- Creative Writing Assistance: AI tools can assist human writers by suggesting plot ideas, character development, and stylistic changes. These tools can act as collaborators, helping writers refine their work and explore new creative directions.
- Interactive and Immersive Art:
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: AI is used in virtual and augmented reality (VR and AR) to create interactive art experiences. AI-driven systems can adapt and respond to user interactions, creating immersive and dynamic artistic environments.
- Generative Installations: AI can be integrated into art installations to generate real-time visual or auditory experiences based on user input or environmental factors. These installations can offer unique and personalized artistic encounters.
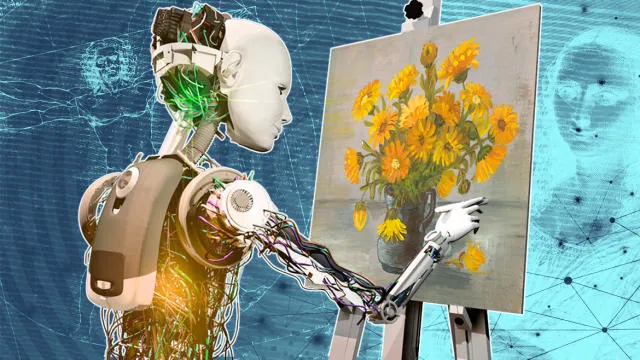
Benefits of AI in Art and Creativity
- Expanded Creative Possibilities:
- Innovation: AI opens up new possibilities for artistic innovation by enabling the exploration of novel styles, techniques, and forms. Artists can use AI to experiment with concepts that may be difficult or time-consuming to achieve through traditional methods.
- Creative Collaboration: AI serves as a collaborative partner, allowing artists to combine their skills with machine-generated creativity. This partnership can lead to unexpected and exciting outcomes that push the boundaries of traditional artistic practices.
- Increased Accessibility:
- Democratization of Art: AI tools lower the barrier to entry for artistic creation, allowing individuals without formal training to produce high-quality art. AI-driven applications enable people from diverse backgrounds to express their creativity and participate in the art world.
- Customization and Personalization: AI enables the creation of personalized artistic content tailored to individual preferences. Users can generate custom artworks, music, and writings based on their tastes, leading to more meaningful and engaging experiences.
- Efficiency and Productivity:
- Accelerated Creation: AI can automate certain aspects of the creative process, such as generating variations of artwork or composing background music. This efficiency allows artists to focus on higher-level creative decisions and accelerates the production process.
- Enhanced Creativity: By handling repetitive or technical tasks, AI frees up artists to explore new ideas and experiment with innovative approaches. This enhanced creative freedom can lead to the development of unique and groundbreaking artistic works.
Challenges and Considerations
- Authenticity and Originality:
- Debate Over Authenticity: The use of AI in art raises questions about the authenticity and originality of machine-generated works. Some argue that AI lacks the emotional depth and personal experience of human artists, which may affect perceptions of artistic value.
- Attribution and Ownership: Determining the authorship and ownership of AI-generated content can be complex. As AI systems create art based on existing data, issues related to intellectual property and credit may arise.
- Ethical and Bias Concerns:
- Bias in AI Systems: AI systems can inherit biases present in the training data, leading to biased or stereotypical outputs. Ensuring that AI-generated art is inclusive and free from harmful biases requires careful consideration and oversight.
- Ethical Use: The ethical use of AI in art involves addressing concerns related to the manipulation of existing works and the potential for misuse. Establishing guidelines and ethical standards for AI-driven creativity is essential for responsible implementation.
- Technical Limitations:
- Quality and Coherence: While AI has made significant strides, achieving the same level of quality and coherence as human-created art remains challenging. Technical limitations may impact the effectiveness and appeal of AI-generated content.
- Dependence on Data: AI systems rely on large datasets for training, and the quality of the generated content is influenced by the quality of the input data. Ensuring diverse and representative datasets is crucial for producing meaningful and inclusive art.
The Future of AI in Art and Creativity
- Advancements in AI Technology:
- Improved Algorithms: Ongoing advancements in AI algorithms and models will enhance the capabilities of AI in art and creativity. Future developments may lead to more sophisticated and nuanced creative outputs, expanding the possibilities for artistic expression.
- Integration with Emerging Technologies: Combining AI with emerging technologies, such as blockchain and IoT, may offer new ways to interact with and experience art. These integrations could lead to innovative and interactive artistic experiences.
- Collaboration and Innovation:
- Human-AI Collaboration: The future of AI in art will likely involve deeper collaboration between human artists and AI systems. This partnership can foster innovation and lead to the creation of new artistic forms and genres.
- Exploration of New Mediums: AI will continue to drive exploration and experimentation with new artistic mediums and formats. Artists and technologists will collaborate to push the boundaries of what is possible in creative expression.
- Ethical and Societal Impact:
- Ethical Guidelines: Developing ethical guidelines and frameworks for the use of AI in art will be essential for addressing concerns related to authenticity, bias, and intellectual property. Ensuring responsible and equitable use of AI will shape the future of creative practices.
- Cultural and Social Implications: The integration of AI into art will have cultural and social implications, influencing how art is created, perceived, and valued. Understanding and addressing these implications will be important for fostering a positive and inclusive artistic landscape.

Conclusion
AI is reshaping the landscape of art and creativity, offering new possibilities for artistic expression and collaboration. By leveraging advanced technologies such as machine learning and neural networks, AI is enabling the creation of innovative and personalized content across various artistic domains. While challenges related to authenticity, ethics, and technical limitations remain, the future of AI in art holds great promise. As technology continues to evolve, AI will play an increasingly significant role in pushing the boundaries of creativity and transforming the way we experience and engage with art.