In recent years, mental health apps have emerged as a powerful tool for supporting mental wellbeing, offering users a range of services from stress management to therapeutic interventions. These digital platforms provide accessible, scalable, and often personalized approaches to mental health care. As mental health becomes a growing priority for many individuals, mental health apps are playing an increasingly vital role in enhancing and supporting psychological wellness. This article explores the evolution of mental health apps, their benefits, features, and considerations for effective use.

Evolution of Mental Health Apps
Mental health apps have evolved significantly since their inception. Initially, they focused on basic self-help resources and mood tracking, but today’s apps offer a comprehensive suite of tools designed to address various aspects of mental health.
- Early Beginnings: Early mental health apps were primarily designed for mood tracking and providing general mental health information. They offered limited interactivity and were often standalone tools.
- Advancements in Technology: With the rise of smartphones and advanced technologies, mental health apps began to incorporate features such as guided meditation, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) exercises, and personalized feedback.
- Integration of AI and Data: Modern mental health apps leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics to provide tailored recommendations, real-time support, and advanced therapeutic techniques. These advancements have made apps more effective and user-centric.
- Teletherapy and Support: Many apps now offer direct access to mental health professionals through teletherapy, enabling users to receive professional support and counseling from the comfort of their homes.
Benefits of Mental Health Apps
- Accessibility: Mental health apps provide easy access to mental health resources and support, making it possible for individuals to seek help without geographical or financial barriers. This is particularly beneficial for those in remote areas or with limited access to traditional mental health services.
- Convenience: Users can access mental health tools and support anytime and anywhere, fitting mental health care into their schedules and lifestyles. This convenience makes it easier for individuals to engage in regular self-care practices.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many mental health apps offer free or low-cost options compared to traditional therapy, making mental health support more affordable and accessible to a wider audience.
- Personalization: Advanced apps use data and AI to personalize content and recommendations based on individual needs, preferences, and progress. This personalized approach enhances the relevance and effectiveness of the support provided.
- Privacy and Anonymity: Mental health apps often provide a sense of privacy and anonymity, which can reduce the stigma associated with seeking help. Users may feel more comfortable exploring mental health issues and seeking support in a private setting.
- Self-Management: Apps offer tools for self-management and self-care, such as mood tracking, relaxation exercises, and cognitive-behavioral techniques. These tools empower users to take an active role in managing their mental health.
- Monitoring and Progress Tracking: Mental health apps often include features for tracking progress and monitoring mental health metrics. This allows users to observe patterns, identify triggers, and assess the effectiveness of their interventions.
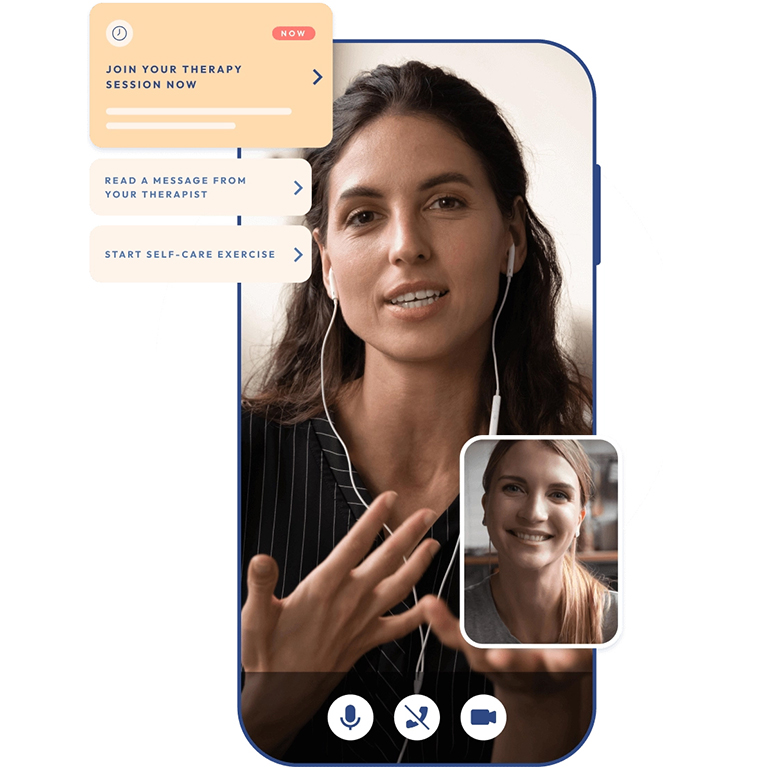
Key Features of Mental Health Apps
- Mood Tracking: Many apps include mood tracking features that allow users to log their emotions, identify patterns, and gain insights into their mental health. This information can be useful for self-awareness and identifying areas that may require attention.
- Therapeutic Exercises: Apps often provide guided therapeutic exercises, such as mindfulness meditation, CBT exercises, and relaxation techniques. These exercises help users manage stress, anxiety, and other mental health issues.
- Teletherapy and Counseling: Some apps offer access to licensed therapists and counselors through secure video calls, messaging, or voice calls. This feature provides users with professional support and guidance.
- Educational Content: Mental health apps may include educational resources on mental health topics, such as articles, videos, and interactive content. This content helps users understand mental health issues and learn coping strategies.
- Goal Setting and Reminders: Apps often include features for setting mental health goals and receiving reminders for self-care activities. This helps users stay engaged with their mental health routines and maintain consistency.
- Community Support: Many apps provide access to online communities or forums where users can connect with others facing similar challenges. This sense of community can offer support, encouragement, and shared experiences.
- Customization and Personalization: Apps use algorithms and user input to offer personalized recommendations and content based on individual needs and preferences. Customization enhances the relevance of the app’s features and support.
Considerations for Using Mental Health Apps
- Privacy and Security: Users should ensure that the app they choose has robust privacy and security measures in place to protect their personal information and data. Check for encryption, secure login methods, and clear privacy policies.
- Professional Oversight: While mental health apps can offer valuable support, they should not replace professional therapy or medical advice. Users experiencing severe mental health issues should seek guidance from licensed mental health professionals.
- App Quality and Evidence-Based Approaches: Evaluate the quality and credibility of the app by reviewing its evidence-based approaches, user reviews, and any endorsements from mental health professionals.
- User Engagement: Success with mental health apps often depends on consistent engagement and usage. Users should be committed to actively using the app’s features and incorporating them into their daily routines.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Consider whether the app addresses cultural and language needs relevant to the user. Mental health apps should be inclusive and respectful of diverse backgrounds and experiences.
- Technical Issues: Be aware of potential technical issues, such as app crashes or compatibility problems. Regular updates and maintenance from the app developer can help address these issues.
- Cost and Accessibility: Evaluate the cost of the app and any additional features or subscriptions required. Ensure that the app is affordable and accessible to users with different financial situations.

Conclusion
Mental health apps are revolutionizing how individuals manage and support their mental health, providing accessible, convenient, and personalized tools for self-care and professional support. With features ranging from mood tracking and therapeutic exercises to teletherapy and community support, these apps offer valuable resources for improving mental wellbeing. However, users should be mindful of privacy concerns, app quality, and the importance of professional guidance when needed. By integrating mental health apps into their routines and making informed choices, individuals can enhance their mental health journey and overall quality of life in the digital age.


